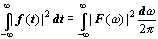Intuitively, if the Fourier
transform has a large magnitude over a frequency range
then the signal has
significant energy over that range
And if the magnitude of the
Fourier transform is zero (or† very
small) then the
signal has no significant
energy in that range