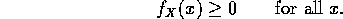Next: Properties of Continuous
Up: Essentials of Probability
Previous: Poisson Random Variable
-
So far we have focused on discrete(-valued) random variables,
e.g.
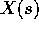 must be an integer.
must be an integer.
-
Examples of discrete random variables:
- The number of arrivals in one second.
- The number of attempts until success.
-
A continuous-valued random variable takes on a range of real values,
e.g.
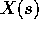 ranges from 0
to
ranges from 0
to  as s varies.
as s varies.
-
Examples of continuous(-valued) random variables:
- The time when a particular arrival occurs.
- The time between consecutive arrivals.
-
A discrete random variable has a
``staircase" CDF.
-
A continuous random variable has (some) continuous slopes to its CDF.
-
Thus, for a continuous random variable X, we can define its
probability density function (pdf) by
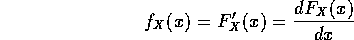
-
Note that since
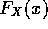 is non-decreasing in x, we have
is non-decreasing in x, we have
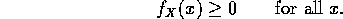
Ken Vastola
Fri Mar 15 14:12:07 EST 1996
 must be an integer.
must be an integer.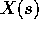 ranges from 0
to
ranges from 0
to 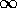 as s varies.
as s varies.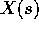 must be an integer.
must be an integer.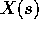 ranges from 0
to
ranges from 0
to  as s varies.
as s varies.
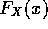 is non-decreasing in x, we have
is non-decreasing in x, we have