



Next: Properties of a
Up: Inside an IMP
Previous: Applications of Queueing
-
A Poisson process is a sequence of events ``randomly spaced in time."
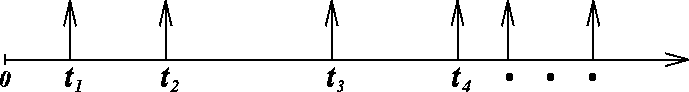
- Examples
-
Customers arriving to a bank.
- Geiger counter clicks
- Packets arriving to a buffer.
- The rate
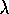 of a Poisson process is the average number of events per unit time
of a Poisson process is the average number of events per unit time
(over a long time).

-
To develop a deeper understanding of modeling real world events
using the Poisson process,
click here.
- To learn more about the mathematics of the Poisson process,
follow the links below or follow the
 button.
button.
Ken Vastola
Fri Mar 15 14:12:07 EST 1996
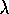 of a Poisson process is the average number of events per unit time
of a Poisson process is the average number of events per unit time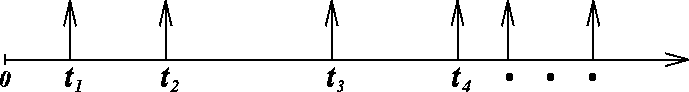
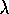 of a Poisson process is the average number of events per unit time
of a Poisson process is the average number of events per unit time